・IT/Web系エンジニアの経験者の方
・どこの転職エージェントを利用しようか迷っている方
それなら、キッカケエージェントにご相談!
キッカケエージェントでは、少数精鋭のエージェントが、エンジニアの経験やスキル、志向性などをカウンセリングし、的確なアドバイスを提供します!
また、徹底した企業へのヒアリングにより、最適なマッチングを実現し、今では内定率が一般的なエージェントの2倍以上となっています!
転職エージェントに迷っている方、まずは無料でキャリア相談から!
(この記事は2023年11月03日に投稿されました。)
Node.jsでサーバー側にて操作したコンテンツをページに表示するにはejsを使用します。
ejsとはNode.jsで使用できるテンプレートエンジンにになります。
そのため、ejsを使用することでJavaScript側で操作したコンテンツをWebページ上に表示することができるようになります。
また、読み込んだURLによって表示するファイルを操作することもできるため、動的にWebページを表示したい場合はejsを使用するようにしましょう。
今回はNode.jsのejsでページのコンテンツを動的に表示する方法について紹介していきます。
Node.jsでWebページを動的に読み込んで表示したい場合
Node.jsとは
Node.jsとは、JavaScriptでサーバーサイドの環境を実行することができる、オープンソースのランタイム環境となります。
非常に幅広い用途に適しており、特にWebアプリケーションのバックエンド、APIサーバー、リアルタイムアプリケーションの開発に使用されています。

ejsとは
ejsとは、「Embedded JavaScript Templates」といい、Node.jsで使用するテンプレートエンジンになります。
こちらは、Node.jsでは標準では準備されていないため、Nodeをインストールするだけでは使用できません。
そのため、Nodeのインストール後に別でejsをインストールする必要があります。
ejsの使い方
ejsは下記のような流れで使用することができます。
ejsをインストール
まず、ejsをインストールします。
インストールを行うにはコマンドプロンプトやターミナルで下記のようなコマンドを入力します。
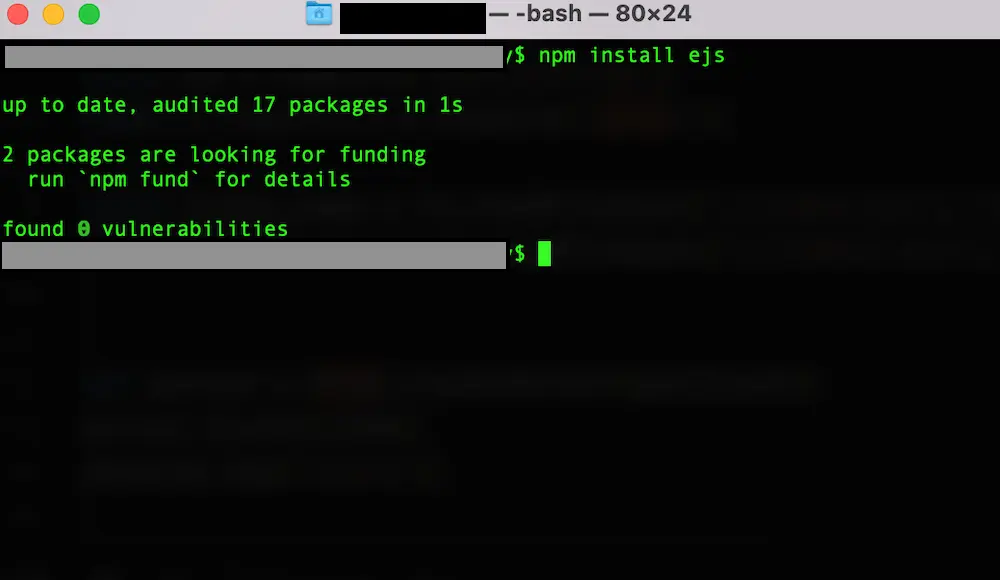
1 | npm install ejs |
すると下記のような画像が表示されます。
また、package.jsonを開くと、「ejs: バージョン名」が追加されるようになります。
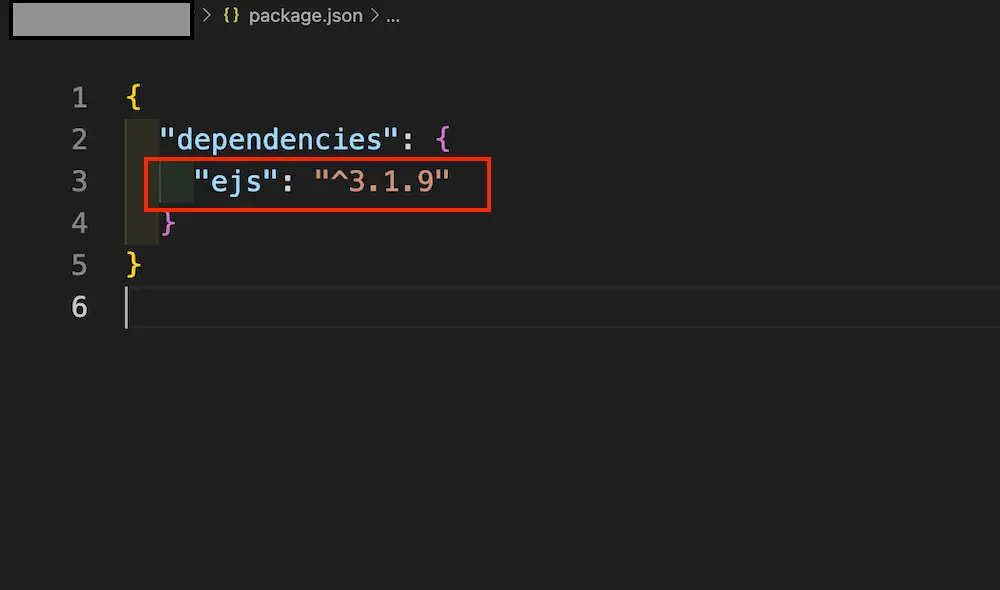
ここまで確認ができると、ejsのインストールは完了です。
ejsファイルを作成
ejsのインストールが完了したら、エディターアプリ、もしはファイルにてejsファイルを作成します。
今回はNode.jsを使用するjsファイルと同じ階層に「sample.ejs」と名前を付けたファイルを作成します。
ファイルの作成ができましたら、ファイルの中身に下記のコードを入力します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ja"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>ejsファイルの作成</title> </head> <body> <h2>ここはsample.ejsファイルのデータになります。</h2> <p>sample.ejsの中身が表示されているよ。</p> </body> </html> |
ここまでできましたら、ejsファイルの作成は完了です。
ejsファイルを読みこむ
ejsファイルの作成が完了しましたら、作成したejsファイルを読み込んでいくようにします。
「sample.ejs」と同じ階層に「main.js」を作成し、下記のコードを入力します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | const http = require("http"); const fs = require("fs"); //ejsを読み込む const ejs = require("ejs"); // 作ったejsファイルを読み込む const template = fs.readFileSync("./sample.ejs", "utf-8"); |
require(“ejs”)でejsモジュールを読み込みます。
そして、読み込んだからreadFileSync()を使用して指定したejsファイルを読み込みます。
ejsのデータを受け取る
ejsファイルを読み込むことができましたら、読み込んだファイルを受け取ります。
先ほど記載した「main.js」に続きとして下記の「ここから下を追記」から下のコードを追記します。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | const http = require("http"); const fs = require("fs"); //ejsを読み込む const ejs = require("ejs"); // 作ったejsファイルを読み込む const template = fs.readFileSync("./sample.ejs", "utf-8"); // ここから下を追記 const server = http.createServer(renderData); server.listen(3200); function rendertData(request, response) { //レンダリング const html = ejs.render(template); response.writeHead(200, { "content-Type": "text/html" }); response.write(html); response.end(); }); |
render()で指定したejsファイルのデータを受け取り、HTMLのソースコードに変換して表示しています。
これで、ejsの使い方は完了です。
ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に表示するサンプルコード
ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に表示するサンプルコードをご紹介します。
ここでは、下記の2パターンでejsを使用します。
- 指定したejsファイルをが存在する場合
- 指定したejsファイルをが存在しない場合
指定したejsファイルをが存在する場合
指定したejsファイルが存在する場合は、指定したejsファイルのデータ読み込んで画面に表示します。
● index.ejs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h1>index</h1> <p>これはindex.htmlのページです。</p> </body> </html> |
● main.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') const ejs = require('ejs') const index_page = fs.readFileSync('./index.ejs', 'UTF-8') var server = http.createServer(index_format) server.listen(3200) function index_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res let content = ejs.render(index_page) response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } |
実行結果
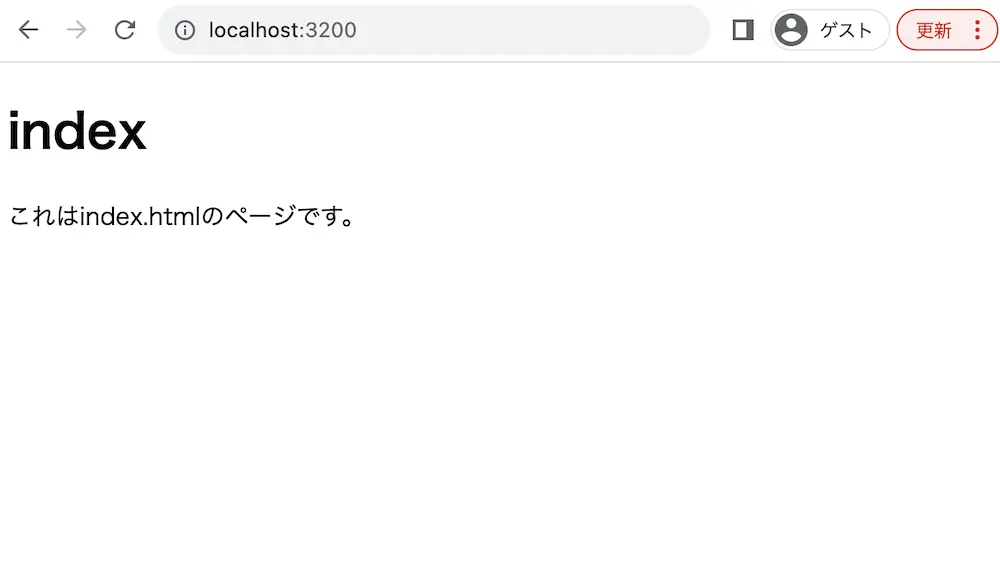
ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に表示しています。
そのため、index.ejsに記載されている内容がHTML要素となってWebページで表示されています。
指定したejsファイルをが存在しない場合
指定したejsファイルが存在しない場合は、エラーの画面を表示します。
● index.ejs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h1>index</h1> <p>これはindex.htmlのページです。</p> </body> </html> |
● main.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') const ejs = require('ejs') const index_page = fs.readFileSync('./index2.ejs', 'UTF-8') var server = http.createServer(index_format) server.listen(3200) function index_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res let content = ejs.render(index_page) response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } |
実行結果
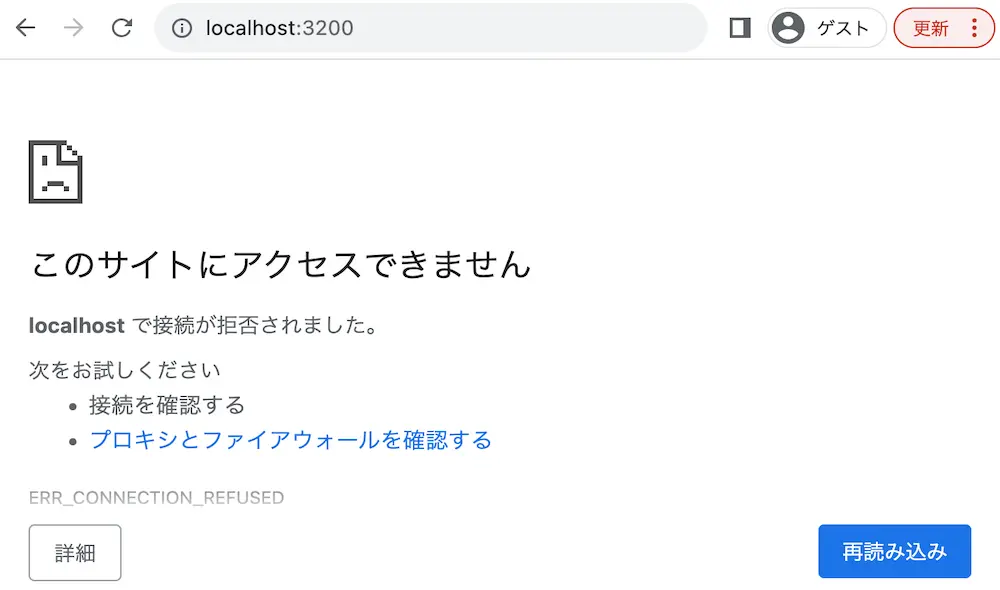
ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に表示しています。
今回は「index2.ejs」を読み込もうとしてますが、存在しないためエラー画面が表示されています。
ejsで処理した値をページのコンテンツとして動的に表示する方法
ejsで処理した値をページのコンテンツとして動的に表示するにはejsファイルに「<% %>」を使用します。
「<% %>」の中はejsの独自機能になりますので、こちらでかこまれたコードはJavaScriptとして読み取ることができます。
そのため「<% %>」を使用することで、ejsでサーバー側にて処理した値を表示することが可能になります。
ここでは、下記の2パターンで「<% %>」を使用します。
- 設定した値をHTML要素として表示する場合
- HTML要素を動的に作成する場合
設定した値をHTML要素として表示する場合
設定した値をHTML要素として表示するには開始タグと終了タグ内に<%= 変数 %>を追記します。
● index.ejs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h1><%= title %></h1> <p><%= content %></p> </body> </html> |
● main.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') const ejs = require('ejs') const index_page = fs.readFileSync('./index.ejs', 'UTF-8') var server = http.createServer(index_format) server.listen(3200) function index_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res let content = ejs.render(index_page, { title: "indexのページ", content: "ここはindex.ejsの中身が表示されます。" }); response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } |
実行結果
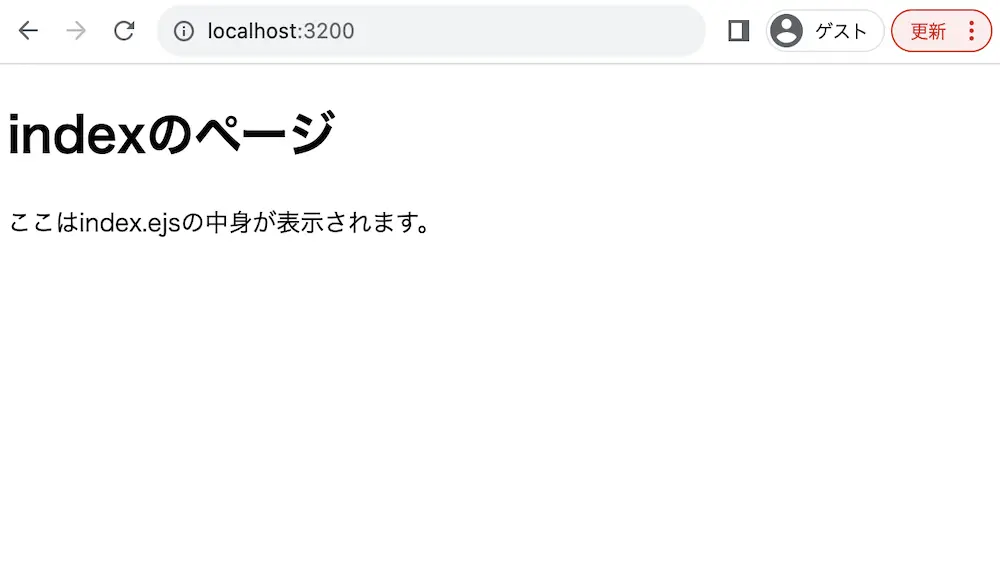
ejsで設定した値をHTML要素として表示しています。
そのため、h1タグ要素には「title」変数の値が、pタグ要素には「content」変数の値が表示されています。
HTML要素を動的に作成する場合
HTML要素を動的に作成するには「<% %>」に実行するスクリプトを追記します。
● index.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h1><%= title %></h1> <table> <% for(let key in data) { %> <tr> <th><%= key %></th> <th><%= data[key] %></th> </tr> <% } %> </table> </body> </html> |
● main.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | let data = { name: "山田 太郎", romeName: "Yamada Taro", old: "25", gender: "男", phone: "090-XXXX-XXXX", from: "東京", hobby: "サウナ" } const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') const ejs = require('ejs') const index_page = fs.readFileSync('./index.ejs', 'UTF-8') var server = http.createServer(index_format) server.listen(3200) function index_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res let content = ejs.render(index_page, { title: data.name + "のページ", data:data }); response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } |
実行結果
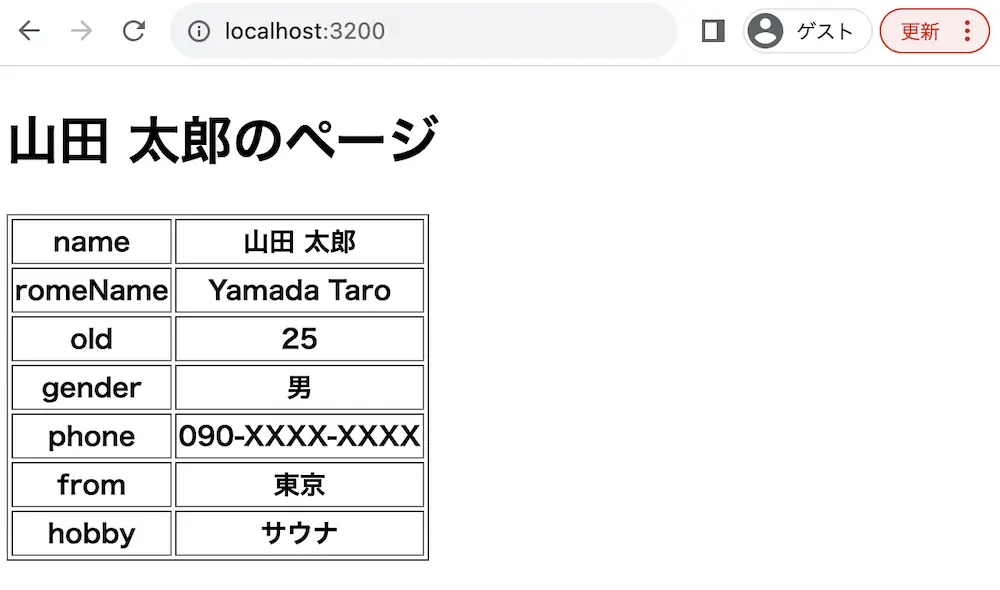
ejsでHTML要素を動的に作成しています。
今回はejsファイルでfor-in文を使用し、table要素の項目を作成しています。
そのため、オブジェクトのデータがtable要素となって表示されています。
ejsでJSONデータをページのコンテンツとして動的に表示する場合
ejsでJSONデータをページのコンテンツとして動的に表示するにはJSON.parse()を使用します。
JSON.parse()とは、JSONデータをデコードするメソッドとなります。
そのため、ejsでJSONデータを受け取り、デコードすることで、JSONファイルを読み込むことができるようになります。
● index.ejs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title><%=title %></title> </head> <body> <h1><%=title %></h1> <table border="1"> <thead> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>名前</th> <th>教科</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <% for(i= 0; i < contents.teacher.length; i++) { %> <tr> <th><%=contents.teacher[i].id %></th> <th><%=contents.teacher[i].name %></th> <th><%=contents.teacher[i].job %></th> </tr> <% } %> </tbody> </table> </body> <style> h1 { font-size: 40px; text-align: center; margin: 0px; } table{ font-size: 20px; width: 80%; } body { font-size: 14px; margin: 5px } </style> </html> |
● index.json
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | { "teacher":[ {"id": "DCT0034789","name": "田中XX","job": "数学"}, {"id": "DCT0035589","name": "鈴木YY","job": "国語"}, {"id": "DCT0032389","name": "田中ZZ","job": "理科"}, {"id": "DCT0023789","name": "木村AA","job": "社会"}, {"id": "DCT0010789","name": "高井BB","job": "英語"} ] } |
● main.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') const ejs = require('ejs') const index_page = fs.readFileSync('./index.ejs', 'UTF-8') const index_json = fs.readFileSync('./index.json', 'UTF-8') var server = http.createServer(index_format) server.listen(3200) function index_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res const dataJSON = index_json.toString() const data = JSON.parse(dataJSON) let content = ejs.render(index_page, { title: "JSONデータを受け取る", contents: data }); response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } |
実行結果
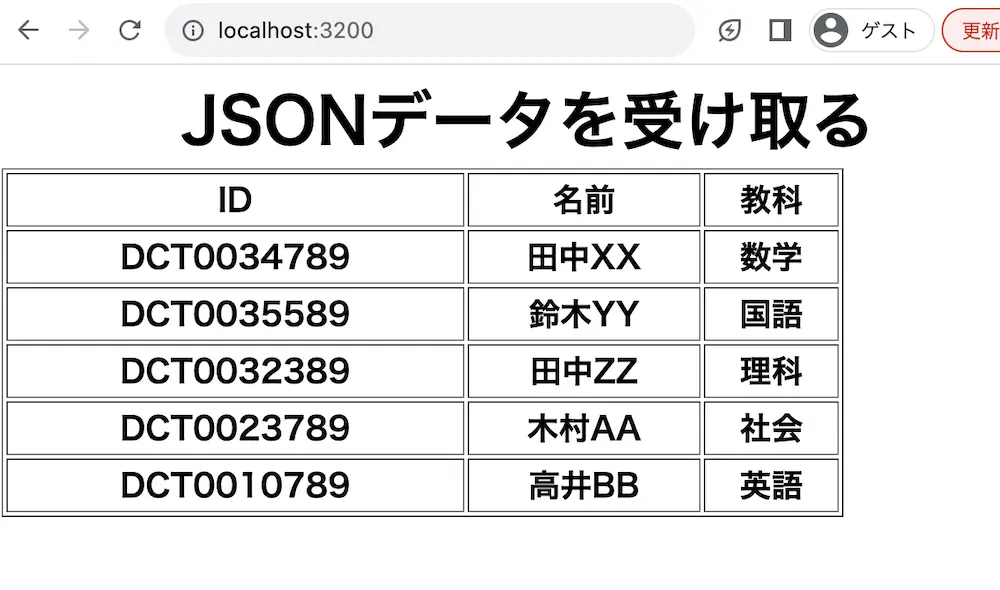
ejsでJSONデータをページのコンテンツとして動的に表示しています。
今回はJSONデータをJSON.parse()にてオブジェクトに変更し、オブジェクトのデータをejsファイルで受け取っています。
そのため、JSONファイルのデータがtable要素となって表示されています。
ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に切り替えて表示する場合
ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に切り替えて表示するにはURLオブジェクトを使用します。
URLオブジェクトを使用することで、読み込んだURLを文字列して取得することができます。
つまり、読み込んだURLを条件にすることで表示するejsファイルを変更することが可能になります。
● index1.ejs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title><%=title %></title> </head> <body> <h1><%=title %></h1> <p><%=content %></p> <p><a href="/index2">index2に移動</a></p> </body> <style> h1 { font-size: 40px; text-align: center; margin: 0px; } p{ font-size: 20px; } body { font-size: 14px; margin: 5px } </style> </html> |
● index2.ejs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="jp"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title><%=title %></title> </head> <body> <h1><%=title %></h1> <p><%=content %></p> <p><a href="/">index1に戻る</a></p> </body> <style> h1 { font-size: 40px; text-align: center; margin: 0px; } p{ font-size: 20px; } body { font-size: 14px; margin: 5px } </style> </html> |
● main.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | const http = require('http') const fs = require('fs') const ejs = require('ejs') const url = require('url') const index1_page = fs.readFileSync('./index1.ejs', 'UTF-8') const index2_page = fs.readFileSync('./index2.ejs', 'UTF-8') var server = http.createServer(renderData) server.listen(3200) console.log('start') function renderData(request, response){ let url_parts = url.parse(request.url, true) switch (url_parts.pathname) { case '/': index1_format(request, response, url_parts) break; case '/index2': index2_format(request, response) break; default: response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.end('no-page'); } } function index1_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res let msg = "index1のページが表示されています。" let content = ejs.render(index1_page, { title: 'index1のページ', content: msg, }) response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } function index2_format(req, res) { let request = req let response = res let msg = "index2のページが表示されています。" let content = ejs.render(index2_page, { title: 'index2のページ', content: msg, }) response.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'}) response.write(content) response.end(); } |
実行結果

URLオブジェクトでejsのページのコンテンツを動的に切り替えて表示しています。
今回はswitch-case文を使用して、取得したURLによって受け取るejsファイルのデータを変更しています。
そのため、「index2に移動」をクリックすると、index2.ejsのページが表示され、「index1に戻る」をクリックすると「index1.ejs」のページが画面に表示されています。
まとめ
⚫︎ Node.jsとは、JavaScriptでサーバーサイドの環境を実行することができる、オープンソースのランタイム環境である。
⚫︎ ejs(Embedded JavaScript Templates)とは、Node.jsで使用するテンプレートエンジンである。
⚫︎ 指定したejsファイルが存在する場合は、指定したejsファイルのデータを画面に表示する。
⚫︎ 指定したejsファイルが存在しない場合は、エラーの画面を表示する。
⚫︎ ejsで処理した値をページのコンテンツとして動的に表示するにはejsファイルに「<% %>」を使用する。
⚫︎ 設定した値をHTML要素として表示するには開始タグと終了タグ内に<%= 変数 %>を追記する。
⚫︎ HTML要素を動的に作成するには「<% %>」に実行するスクリプトを追記する。
⚫︎ ejsでJSONのデータをページのコンテンツに表示するには、JSON.parse()を使用する。
⚫︎ ejsでページのコンテンツを動的に切り替えて表示するにはURLオブジェクトを使用する。
 Sossyの助太刀ブログ
Sossyの助太刀ブログ 

